Osram Improves Efficiency of Blue LED Chips by Reducing Forward Voltage
Osram Opto Semiconductors has achieved one of the best values in the world in terms of forward voltage for blue high-current chips. This has led to an increase in efficiency of up to eight percent. Optimized InGaN chips (Indium-Gallium-Nitride) featuring UX:3 chip technology are the basis for blue or white LEDs – and are already used in production. Osram experts also see considerable potential for reducing the value by a further 20 to 30 millivolts (mV) by the summer of 2015 – offering a further boost in efficiency.
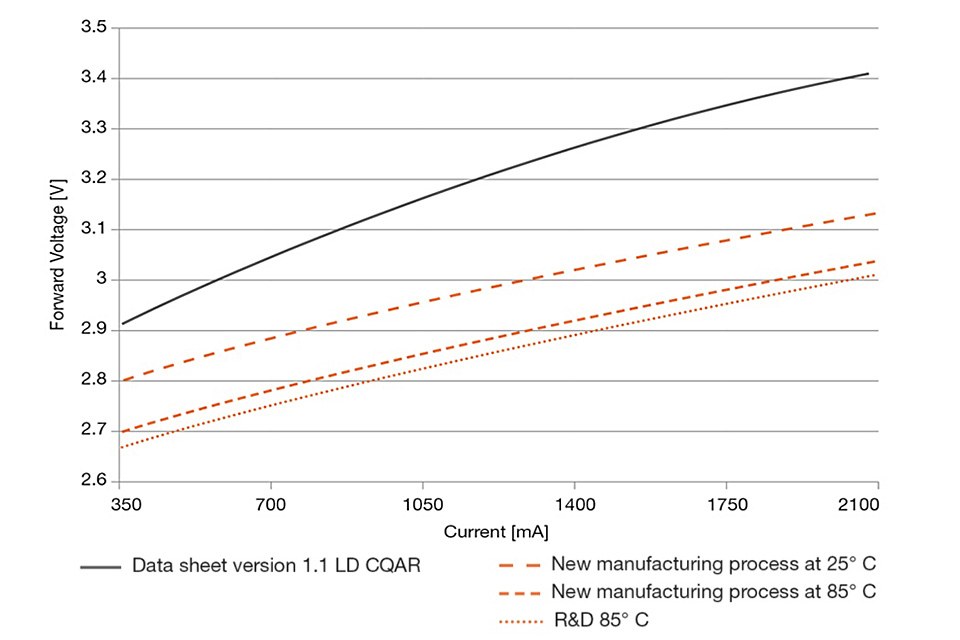
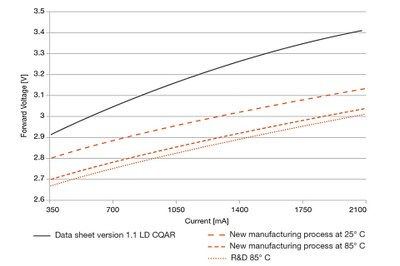
The blue Osram Oslon Square (LD CQAR), for example, now has a typical forward voltage of only 2.87 volts (V) instead of the 3.05 V specified so far in the data sheet – the lowest typical values in this component class worldwide. At 85° C a voltage of 2.78 V can be achieved in the component. Depending on the operating point, this translates into an increase in efficiency of these light emitting diodes (LEDs) of six to eight percent, which can be transferred to the entire UX:3 chip family. These chips can be found in all blue and white LEDs. The LEDs are used in an extremely wide range of applications – the Osram Oslon Square, for example, in street lighting and industrial lighting. “The reduction in forward voltage was achieved thanks to a new process in the epitaxy”, said Dr. Marcus Eichfelder, Project Manager at the Regensburg high-tech company. Production of the first optimized chips started back in August 2014.
The next steps: further development and transfer to production
There is still enormous potential. “In the laboratory we have already succeeded in further reducing the forward voltage by as much as 30 mV”, said Dr. Joachim Hertkorn, Epitaxy expert at Osram Opto Semiconductors. This would improve the efficiency of the LED chips by a further percentage point. “In view of the speed with which this first step has been implemented, we are confident that the improved process can be transferred to production by the summer of 2015”, added Hertkorn. “Any further reductions in forward voltage will then only be marginal owing to the laws of physics.”
About Osram Opto Semiconductors:
Osram, with its headquarters in Munich, is one of the two leading lighting manufacturers in the world. Its subsidiary, Osram Opto Semiconductors GmbH in Regensburg (Germany), offers its customers solutions based on semiconductor technology for lighting, sensor and visualization applications. Osram Opto Semiconductors has production sites in Regensburg (Germany), Penang (Malaysia) and Wuxi (China). Its headquarters for North America is in Sunnyvale (USA). Its headquarters for the Asia region is in Hong Kong. Osram Opto Semiconductors also has sales offices throughout the world. For more information go to www.osram-os.com.